It feels like half of the population runs websites. Nowadays, this is also quite simple – various, freely available CMS tools and website building block systems enable even laymen to create visually appealing websites with just a few mouse clicks. Integrating pictures, texts and graphics is child’s play. And yet there is a problem: A page can be functional and beautifully designed, but if potential visitors do not find it when searching on Google or other search engines, it is useless.
Professional search engine optimisation (SEO) is indispensable in order to make websites visible and searchable for a broad mass of Internet users. The optimisation for search engines consists of two parts – on-page optimisation and off-page optimisation.
If you work in the SEO area yourself or are looking for a position as SEO Manager at an online company, you should recognise the optimisation potential of websites and social media sites, and be able to optimise them for search engines, both on- and off-page.
In this article, we want to deal intensively with the topic of on-page optimisation and clarify important framework conditions for successful search engine optimisation.
The Difference Between On-page and Off-page Optimisation
What is the difference between on-page optimisation and off-page optimisation? As the name suggests, the actual work involved in off-page optimisation takes place outside the relevant Web page. The aim is to increase the reputation of the site, which means – above all – the ranking which search engines like Google assign to a website. This goal is achieved primarily through link building, i.e. the creation of backlinks to the page to be optimised. Backlinks are links that point from the outside to a page, for example to a specific article or an offer. In order to increase the link popularity of a website in this way, both the quantity and the quality of the backlinks are important.
Off-page optimisation is a very complex topic that we’re not going to deal with today. Instead, we are focusing on on-page optimisation.
On-page optimisation is all about SEO optimisation on the website itself. This process starts with a detailed analysis of existing keywords, content and indexing. Once the first inventory has been made, the on-page optimisation is transferred into a continuous workflow, the individual steps of which are conscientiously repeated as long as your website exists.
Some tools can make your job a lot easier and we’ll cover these a little later. For now, we’re going to concentrate on a step-by-step guide that looks at all aspects of on-page optimisation.
Your on-page SEO checklist
Our on-page Optimisation Checklist refers to factors that affect the entire website and those that must be performed for each subpage individually.

Check Indexing
Contrary to popular belief, search engines like Google do not search the entire Internet for a term. Instead, an index of Internet pages is created and the search happens here. Crawlers are used to index the pages and these software-based robots then travel the Internet to search for more websites for the index, where they are sorted and assigned to a hierarchy. This hierarchy has a direct effect on the search engine ranking of an indexed page.
So it’s best to search for your website first and check if and how well it is found. If you can’t find your page at all, there might be a manual penalty in place. This means that you have been de-indexed by the search engine operator. In most cases, this is Google, and you absolutely want to avoid the so-called Google Penalty.
Step 1:
Check the ranking of the most important keywords. Search for the name of the site, the company and some products or services. If the page is not displayed first when searching for unmistakable names, there may be penalties. You can check this in the Google Search Console.
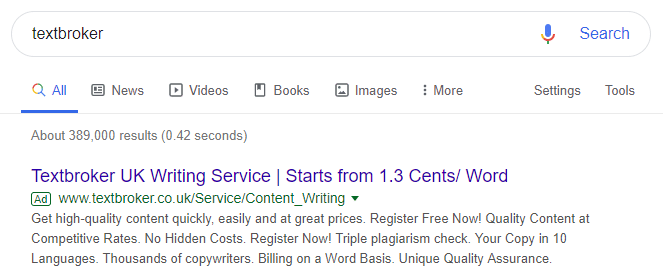
Google search result for “Textbroker”; Source: google.co.uk
Step 2:
Monitor landing pages. With the help of Google Analytics, you can see which of your pages generate organic traffic via search engines and which do not.
The subject of Google Penalty alone is already very extensive. However, if you follow the guidelines of this checklist, you should not have any problems with it. If you do get hit with a Google Penalty, you’ll want to research your options. Software specialist Xovi, for example, has some valuable information for you to consider.

Preventing legal problems
First of all: We can only offer you advice. None of the information offered replaces professional advice from a specialist lawyer. When it comes to legal questions concerning the operation and optimisation of websites, it is always best to seek legal counsel.
Step 1:
In the case of commercial sites, you must observe the imprint obligation which is only not required with purely private websites. The imprint must be clearly visible in the navigation with a maximum of two clicks necessary to access it. In many industries, disclaimers are also necessary – inform yourself exactly about the applicable legal conditions. If a revocation instruction is necessary for your online business, you should make sure it is valid.
Step 2:
Check the privacy statement. This includes, for example, all modules and forms that store personal data and, if instructed, pass it on to external services such as Facebook and other social media. As of 25 May 2018, EU data protection law has undergone a number of changes. Even sole traders and freelancers should now pay close attention to their data protection information.

Optimise indexing and access of search robots
We’ve already talked about search robots. Now it’s time to discuss how you can help the crawlers.
Step 1:
Start by checking the robots.txt file. It sets the access rights for web crawlers to your site. In addition to Google, it’s also a good idea to allow Yahoo, Bing and other search engines free reign. You can use noindex tags to exclude certain areas of your site from access by search robots. Subpages that are no longer needed can also be deleted from the search engine index using the noindex command.
Step 2:
You should also create an XML sitemap that contains a list of all pages in your domain. The XML sitemap can be passed on to search engines to speed up the indexing of your pages.

XML sitemap of textbroker.co.uk
Step 3:
Since not all users have JavaScript enabled in their browsers, you should be able to load content from your site without JavaScript.
Step 4:
Are your CSS and HTML in order? The source code of a website is like the genetic code of a human being. Here, even small problems can have far-reaching effects. Make sure that your source code complies with the current W3C guidelines.

Check the advertising of the site
If you value a high Google Ranking, you should not place too much advertising on your site. Excessive advertising can not only result in poorer search engine rankings but can also deter visitors. This is especially true for advertisements or banners that catch the eye immediately when you visit the site.
Make sure that hidden advertisements are tracked down and deleted. It often happens that hackers smuggle links to external sites or malware into a page. Regular updates are mandatory, especially for CMS systems, in order to close the gateway for hackers.

Side technology – programming knowledge necessary
You can only perform this step yourself if you have the necessary knowledge as a programmer. If in doubt, consult an expert. After all, it’s about manipulating the code, i.e. the genetic make-up of your site.
Step 1:
Use SSL certificates as they make your site more secure, especially when users are asked to enter personal data.
Step 2:
Check IP addresses. If you share your server with other providers, you should check the IP address to make sure that these sites do not engage in unfair business with unauthorised advertising, etc.
Step 3:
Flash is outdated and a potential gateway for viruses. Search engines are now ignoring Flash, so if you’re still using Flash, switch to HTML5.
Step 4:
Search engines can’t find iFrames, so make sure that no content important for search engine ranking is displayed in one.
Step 5:
After a domain change, create 301 redirects. This must be done manually for each URL.
Step 6:
If something is duplicated (we’re still talking about unique content), mark the content in question using canonical tags so that search engines can access the original content.
Step 7:
Clean up unwanted redirects by making sure that they go directly to the destination. For example, through 302 redirects.
Step 8:
Check source code. A page’s code should be uncomplicated, elegant and not unnecessarily long.

Unique content instead of duplicate content
Unique Content is content that is not duplicated. In fact, all content that only appears on your page in the entire web is considered your unique content. Duplicate content, however, is punished by search engines. But apart from the effect on the website ranking, the uniqueness of your texts should also help your visitors with their questions. We will discuss the actual SEO content writing later, but first:
Step 1:
Use only one URL per content. If you cover several different topics on the same subpage, search engines will not “know” which of them they should give more weight to. By assigning content to specific URLs, not only search engine ranking can be influenced. More meaningful subpages generate more traffic, backlinks and shares than topic collections on a single URL.
Step 2:
Do a plagiarism check by searching the Internet regularly for plagiarisms of your content. In case of doubt, you have legal means at your disposal to persuade idea thieves to delete stolen content. In any case, such mostly-unsuspecting users do themselves no favours with plagiarised content as they harm their site by using it. As you will learn later, when creating content via Textbroker, you can be sure to get unique content thanks to automatic plagiarism checking.
Step 3:
Use keywords correctly. In plain text, this means that you should dedicate a separate area to each relevant keyword. Don’t use the same focus keyword on multiple URLs.
Do you need unique content for your website?
Join over 80,000 customers worldwide and use Textbroker for your on-page optimisation.

The structure of the website
This section is about making your site easy for search engines to understand. At the same time, the navigation should also be made easier for visitors to the website.
Step 1:
The URL hierarchy should be structured in such a way that all subpages can be reached with as few clicks as possible. Make sure that URLs are structured in a comprehensible way and without umlauts, as these are still not displayed correctly in many browsers.
Step 2:
Guide your visitors by setting visible links to relevant areas. Every good page has a navigation area with the most important links already easily available.
Step 3:
Do it like Hansel and Gretel: Lay a trail of breadcrumbs! These so-called breadcrumbs show users and search engines the path that has been “followed” to the currently displayed URL.

Breadcrumbs on textbroker.co.uk
Step 4:
Don’t forget the footer as you can also place navigation links here. Especially on pages with many sub-areas, the footer can be used to display numerous links that would otherwise overload the header menu.
Step 5:
Do not neglect link texts! All links can be provided with expressive descriptive texts. This also makes it easier for users and search robots to find relevant areas. It is also important to check links to external pages regularly. If they no longer reach their destination, for example, because the website in question no longer exists, you should delete them.

Maximise page loading speeds
If a website loads too slowly, it can happen that impatient users jump off again. It is therefore important to check the loading times and improve them by compressing them. If you are not familiar with the compression of HTML or JavaScript codes, you should consider consulting an expert.
By using browser caching, the user has the option of specifying how long their browser will store content. By storing the display data, the page loads faster the next time you visit it. The combination of images used several times in CSS sprites also contributes to shorter loading times.
Especially important is the file size of images, which should not exceed 100 kilobytes to allow fast loading of the page. Common graphic tools like Photoshop offer possibilities to edit and save images for the web display.

Google Search Console
The Google Search Console is used by almost all online entrepreneurs and service providers. The tools integrated there can be used with a corresponding account for on-page optimisation.
Step 1:
Remove bad links manually. If there are problems with your links, e.g. with unnatural or purchased links, you can get information from the Search Console and delete the links if necessary.
Step 2:
Can Google get access to your content? You can check in the Search Console.
Step 3:
Deposit an XML Sitemap. This can be done with Google as mentioned above.

Usability of the website
If you want users to feel like visiting your site again, you should optimise the user experience. It’s all about getting your bearings quickly when viewing the site on a desktop PC, tablet or smartphone.
Step 1:
Favicons appear in the browser line as a small icon and mark the website you are currently viewing. In Mozilla Firefox, for example, these favicons can be sorted in a toolbar. Basically, they make it easier for the user to find your site again.
Step 2:
Barrier-free design also allows the visually impaired to participate in the web. So that reading aloud tools can also reproduce the content of images, you must add descriptions to images using alt tags.
Step 3:
Test screenview and resolution because the most important information on each page should be visible without scrolling. Make sure your website is displayed in all popular screen resolutions. See “Responsive Design” below.
Step 4:
Consider weighting. To make navigation easier for visitors, it is best to highlight the most important content. Main business areas – but also references or awards – could be teased directly on the home page.
Step 5:
A call-to-action is used to encourage visitors to take action, such as registering on your website. Use appropriate buttons clearly visible on every relevant page. Be sure to label the buttons clearly so that it is obvious what happens after the click.
Step 6:
Responsive Design. Nowadays, more and more people view websites via smartphones or tablets. In order for the display on mobile devices with the current variety of different screen sizes to function smoothly, websites must be responsive. This means that the layout, including text and images, is smoothly adjusted to the selected screen size and orientation (horizontal or vertical). Ideally, you should check your page in all common screen sizes.
We recommend using analysis tools such as Google Analytics if the mobile version of your online presence differs from the desktop version. To be able to compare the mobile and desktop versions, you will – of course – need to collect data for both separately. It is also advisable to link both versions so that the mobile version points to the desktop version. As described above, you can mark duplicate content with canonical tags.

Other countries, other languages
If your site has different language versions, you must perform all of the on-page actions described above for each of them.
Step 1:
Mark languages in the code with tags. Search engines and browsers recognise the language version by the tags hreflang and rel=”alternate”.
Step 2:
Store languages in the Search Console. To let Google know that your website has different language versions, you should tell it via the Search Console.
Step 3:
Display prices in local currency. International customers will find their way around and won’t have to convert prices first.
Step 4:
Remember to also translate all URLs into the appropriate language.
A quick tip: If you need someone who can write your SEO content in different languages, you will find professional copywriters for various national languages in Textbroker’s pool of authors. We’ll talk a bit more below about how our authoring service can help you improve your website ranking.
Do you need unique content for your website?
Join over 80,000 customers worldwide and use Textbroker for your on-page optimisation.
Read on for measures to be taken on every single URL of your website.

Check keywords
These keywords should correspond to the search terms that are most likely to be used by your target group to find your offer. Start with a keyword analysis and optimise all metadata. This includes adding title tags and description tags to each page.

Optimising URLs
…because these are displayed to the user together with their search result. Speaking URLs contain the main keyword selected for the URL so that users can already see from the URL what awaits them on the page. To make the URL in the browser line easy to read, it should be kept as short as possible.

Check your pages for hacker attacks
Cybercrime is a great evil of our time. Hacker attacks on websites can make them completely unusable, or at least compromise them and have a devastating effect on Google’s ranking. It is therefore important to check your pages for possible hacker attacks and to seek professional help if necessary.

Optimise your content
Unique content on every page
Headings are especially important for longer texts in order to maintain an overview. Search engines can also recognise your headlines and subheadings. It is therefore important to use HTML tags correctly for headlines. The H1 tag may appear only once on each URL. For the other headings, you can use H2, H3 or H4 tags, which are slightly smaller under normal CSS settings. Often the breakdown into H2 headings is sufficient to allow a clean reading flow. H3 and H4 are used to further subdivide particularly long sections.
Keywords denote your important content and are queried in the Google search. LSI keywords, on the other hand, serve to classify the meaning of keywords for Google. For example, the “gate” to the courtyard can be distinguished from the “gate”, which only does stupid things. LSI stands for latent semantic indexing.
Does your content offer real added value to the user? Here we come to the crux of content marketing, because modern search engines are able to capture the informational content of texts. The number of hits and the reactions of users through positive comments or ratings also play a role in website optimisation. When creating your content, always take care to make the interests of your target group and their benefits the maxim of your writing. Highlight your USPs (Unique Selling Points) to engage your visitors and turn them into customers.
Consider factors such as formatting, correct spelling and legibility. Structure texts with meaningful paragraphs and subheadings. Especially for complex topics, a final proofreading is recommended, where spelling – as well as content correctness and reading flow – are optimised. When proofreading and correcting texts, our author service can help you once again.
To find out more about the broad field of content marketings, we recommend that you browse through our Expert Center which offers numerous informative articles.

Optimise images for websites
Let’s not forget the image search on Google and other search engines. For example, if you run a commercial site or blog in areas such as fashion, art or luxury goods, many users will not find your site through a text search, but through images.
In order for search engines to display your images as desired, you should provide them with descriptive file names. Even the image name must tell you what you see on the image. A title tag ensures that the title is displayed in a tooltip during the mouseover effect.
Alt attributes can also be set and are used when the image cannot be displayed. This tag also helps blind and visually impaired users as a browser with the appropriate settings can read the alt text out loud.

Optimise videos for websites
Since the resounding success of YouTube and other video networks, informative or funny clips have played an increasingly important role in commercial self-expression. Accordingly, on-page optimisation also applies to videos used on the website. These can be played in a video player or embedded as a background video.
Basically, you should make sure that your videos are displayed by as many browsers as possible on desktop and mobile devices. Converting all videos to HTML5 is therefore highly recommended.
Similar to image content, the file size of videos should be kept as small as possible to keep page loading speeds high. This can be achieved by reducing resolution and bit rate, for example. However, sound and image quality should not suffer too much.
It makes the most sense to embed as few videos as possible – for example, only background videos – into the page itself. All other video blogs, tutorials or live streams can be published on platforms such as YouTube and linked to your site.

Permanent on-page optimisation
The process of on-page optimisation never ends. Therefore, you should actively track page security and quality control at regular intervals to maintain your high standards. In the following section, we will introduce you to some tools that you can use for on-page optimisation.
Useful Tools for On-page Optimisation
Here’s an overview of the most popular on-page tools you can use to improve your Google ranking and optimise your pages for search engines.
Xovi offers an all-in-one online marketing suite for SEO and social media. Monitor the search engine ranking of your website and the development of your keywords, use a link manager and your own search analyses. Regular analyses of the link profile prevent penalties and helps to correct them. Xovi recommends itself for online shops, agencies and in-house SEO.
Sistrix is an online toolbox for SEO. This allows you to retrieve key figures for each desired domain and analyse their Google rankings. According to the manufacturer, the system itself collects data on practically every domain and has done so since 2008.
At Ryte you will find various tools for better online performance. Ryte Website Success serves to monitor, analyse and optimise websites and offers extensive filter options. Ryte Content Success helps you to create content and can also identify meaningful keywords in other languages. Ryte Search Success is fully focused on the search engine optimisation of your site and provides helpful analysis data in real-time.
Seobility provides tools for easy error analysis for your website, meta- and on-page analysis for each page, as well as duplicate content discovery. Continuous monitoring with reporting is as much a part of the scope as automated crawling.
Audisto is an English-language provider of on-page, content and structural analysis for websites. The powerful Audisto toolset is designed for companies of all sizes. There are no restrictions on how many employees can work with the software.
On-page Optimisation Through Unique Content from Textbroker
Textbroker helps you create unique SEO content by giving you access to a huge pool of capable authors. On Textbroker you’ll find professional copywriters in virtually every field. You can commission them to write SEO articles and create SEO content through a simple order system.
Textbroker’s order mask uses plagiarism software to ensure that your texts are truly unique. With the integrated plagiarism scanner, the plagiarism check already takes place before the author can give you a text. If the plagiariser detects that content is already available on the web, the author must make appropriate changes. This means that you will always receive unique content.
By the way, you can use a protected messenger tool to make direct arrangements with your copywriters and fine-tune the briefing. The briefing itself can already be set in detail via the order mask. Our service team will be happy to assist you with the placement of your first orders.
Register now as a customer and you can place your first orders immediately!
We wish you success with the on-page SEO optimisation of your website pages!
Do you need unique content for your website?
Join over 80.000 customers worldwide and use Textbroker for your on-page optimisation.




No comments available